General
What are the 4C’s of Diamonds?
Previously, people used to compare the diamond’s color with that of river or water to define that diamonds are colorless but the era has changed and so are the aspects of determination. Today, people determine the quality of a diamond with the help of 4C’s. 4C’s stand for a diamond’s cut, color, clarity and carat weight. Here is our blog about 4C’s of diamonds guide so that you understand why these factors play a vital role in assessing the quality of diamonds before buying them.
Diamond Cut:

What is a diamond cut?
The cut confers to how a diamond’s facets collaborate with light. Have you ever observed how many facets a diamond has?
A diamond’s cut confers how well-rounded the measurements of a diamond is, and how these surfaces are arranged to produce shimmer and brilliance.
Why is Diamond Cut important?
Put unambiguously, the cut is subject to the standard of a diamond’s sparkle. If a diamond is cut improperly, it will emerge dull even if it has a high color and clarity grade.
If a diamond is cut well, it will mirror and deflect light for utmost brightness and sparkle. At Padma Jewels, our internal craftsmen are dedicated to innovating the most ingeniously shapely diamonds. This accuracy is what sets Padme Jewels diamonds stand out.
Cut Grades:
There are basically five grading factors: excellent, very good, good, fair, and poor.
• Excellent:
These diamonds are spotlessly cut with the correct segments to boost the blaze, glow, and brilliance in the diamond.
• Very good:
These diamonds are similar to excellent grade diamonds but with less quality.
• Good:
These diamonds are cut in such a manner that yields some glow to the stone, but may be asymmetric in some layers.
• Fair:
Light smoothly enters out through the beneath and edges of a fair grade diamond. For this cause, fair cut diamonds are not suitable for center stones but could be apt for smaller side stones on a ring.
• Poor:
These diamonds are the least favorable and least common.
Types of Cuts:
The authenticity of a diamond comes from the single sides or surfaces of a diamond. There are various methods to feature a diamond, including a brilliant cut, step cut, rose cut, single cut, and more.
• Brilliant Cut:
The brilliant cut is the most renowned facet agreement. It is made of triangular and kite-shaped surfaces, all aligned to enhance brilliance.
The round brilliant diamond, which has 57 to 58 surfaces, is the most amazing of the diamond cuts. Cushion, oval, marquise, pear and heart-shaped diamonds are also cut using the brilliant surfacing style and are identical to the round brilliant.
• Step Cut:
On a step-cut diamond, the majority of the surfaces are aimed collateral to one another. This generates a window into the diamond. Step-cut diamonds are usually very high in clarity because any incorporations are identifiable without acclamation.
Diamond Color:
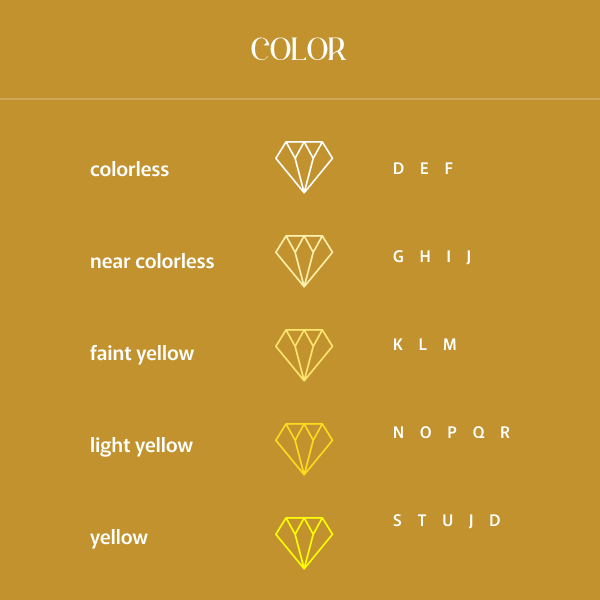
Color relates to the original hue constituted in white diamonds. In nature, most white diamonds have a slight tone of yellow. The industry level for grading color is to estimate each stone against a master set and allocate a letter grade from “D” (colorless) to “Z” (light yellow).
Diamond Color Chart:
Padme Jewels only accepts D color diamonds, E color diamonds, F color diamonds, G color diamonds, H color diamonds and I color diamonds.
DEF
Colorless
GHIJ
Near Colorless
KLM
Faint Yellow
NOPQR
Very Light Yellow
STUVWXYZ
Light Yellow
Diamond Clarity:
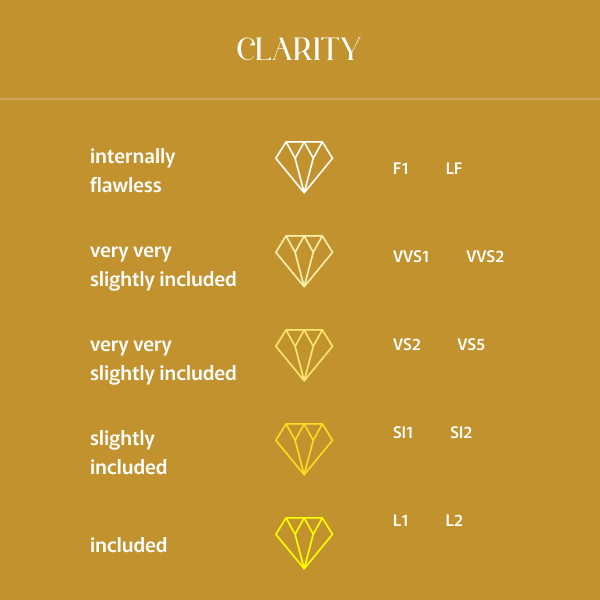
Clarity is the circumstance of being apparent or crystal clear. Diamond clarity is the presence or absence of features called inclusions in the diamond.
When grading the clarity of a diamond, the lab ascertains the respective clarity of the inclusions in a diamond and their consequence on the comprehensive visual look and feel.
Diamond Clarity Chart:
Clarity grade is ascertained on a range of reducing clarity from the top clarity (Flawless or FL) to the lowest clarity (Included 3, or I3).
FL
FL diamonds are Flawless
IF
IF diamonds are Internally Flawless
VVS1 VVS2
VVS diamonds (1 and 2) are Very, Very Slightly Included
VS1 VS2
VS diamonds (1 and 2) are Very Slightly Included
SI1 SI2
SI diamonds (1 and 2) are Slightly Included
I1 I2 I3
I diamonds (1, 2 and 3) are Imperfect
Diamond Carat Weight:

Carat is the part of dimension for the material weight of diamonds. One carat equals 0.200 grams or 1/5 gram and is split into 100 points. For correlation, one carat equals 0.007 ounce massiveness which would need over 2,265 carats to equal 1 pound!
Things to know about Carat:
• Don’t be hesitant to save money:
Choose a carat weight marginally below the whole and half-carat spots. For instance, rather than a 2.00 carat diamond, think of buying a 1.90 carat weight. This will save a substantial amount of bucks, and the slight difference will never be revealed.
• Binge on cut:
This is the most essential factor because it boosts the shine. Even a high-carat diamond with brilliant color and clarity can show up perished and dull if the cut is indigent.
• Lavish shapes cost less per carat:
These are usually less costly than a counterpart round diamond. Alongside, fancy shapes can show up larger than their actual diamond carat weight size, chiefly when set in a halo setting.
The Bottom Line:
When you are aware of all these C’s, it becomes easy for you to choose your ideal diamond ring. This blog was just to inform you about the concepts you were probably unaware of and to enlighten you to make your choices regret-free.

